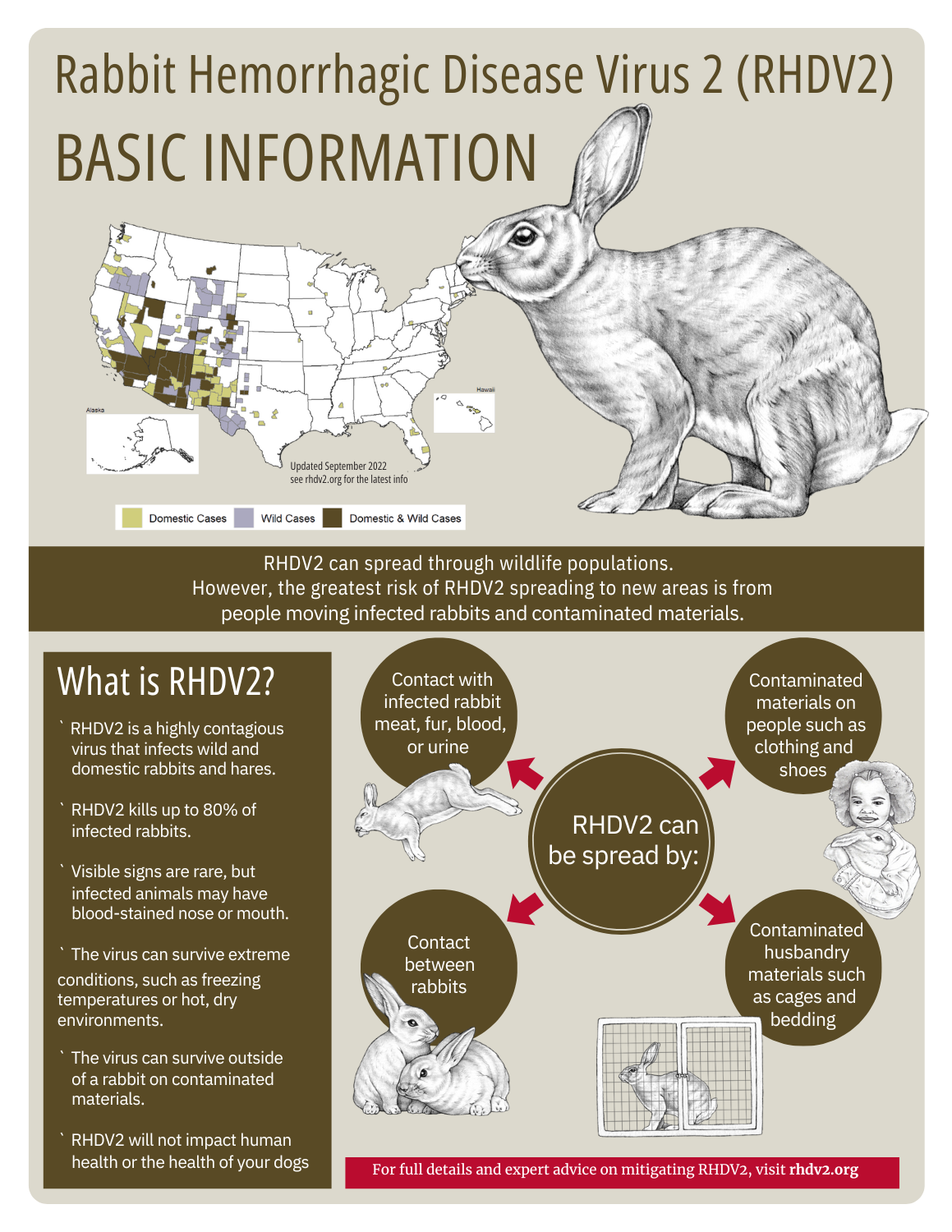
RHDV2
RHDV2 is highly contagious and affects both domestic and wild rabbits. The disease was confirmed in the southwestern US in March 2020 and has continued to spread across multiple states. The RHDV2 virus is very resistant to extreme temperatures. It can be spread through direct contact or exposure to an infected rabbit’s excretions or blood. The virus can also survive and spread from food, water, and any contaminated materials. People can spread the virus indirectly by carrying it on their clothing and shoes. While this virus has not yet reached NC, we recommend that everyone learn about measures to help keep their rabbits safe. A US-made vaccine for RHDV2 has been in development and Medgene Labs has received Emergency Use Authorization.
Symptoms may include
Loss of appetite
Lethargy
High fever
Seizures
Jaundice
Bleeding from nose, mouth, or rectum
Difficulty breathing
Sudden death (most common presentation)
RHDV2 vaccine information:
Veterinarians in North Carolina can now apply for vaccine permits, according to this letter from the NCDA&CS.
Rabbitors is maintaining a list of vaccine availability in each state.
Learn more
RHDV2.org website
Rabbit hemorrhagic disease article on WabbitWiki
RHVD2 resources from The American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA)
RHDV2 regulations in the US article on WabbitWiki
Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease News Network Facebook Group
North Americans RHDV2 Group Facebook Group